JGroups Netty
DISCLAIMER: This project is still experimental and has not been thoroughly tested.
This project uses the Netty framework as the transport layer for JGroups. This is developed by Master’s students from Newcastle University as part of their final project under the supervision of Bela Ban.
Mailing list for questions/issues/comments: [1]
Usage
The JGroups protocol configuration using Netty can be found in netty.xml. The XML file can then be used as the -props field in JGroups. By default use_native_transport is set to false however setting it to true will require a Unix system to work. If the native system is used then then the required tools and libraries must be installed. Instruction for that can be found here.
Taken from Netty
To build the native transport, you need to use Linux with 64-bit kernel 2.6 or higher. Please also install the required tools and libraries:
# RHEL/CentOS/Fedora:
sudo yum install autoconf automake libtool make tar \
glibc-devel libaio-devel \
libgcc.i686 glibc-devel.i686
# Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install autoconf automake libtool make tar \
gcc-multilib libaio-dev
Building the MacOS/BSD native transport
To build the native transport, you need to use MacOS 10.12 or higher. Please also install the required tools and libraries:
brew install autoconf automake libtool
Build and Run
Running ./build.sh will do a maven clean install and copy the dependencies. run.sh will include the dependencies as part of the java classpath argument and can be used to run JGroups.
Example
./build.sh
./run.sh org.jgroups.tests.perf.UPerf -props netty.xml
Implementation Details
The JGroups protocol is implemented in Netty.java which will manage TCP communication to other peers. To understand how this transport layer works, only 2 classes needs to be understood Netty.java and NettyConnection.java
Netty.java
This class is an extension of TP and provides all the details in order for the JGroups stack to integrate with Netty. Netty.java will create a NettyConnection by passing an instance of NettyReceiverListener which has callbacks for onReceive and onError. These methods are fired when a message is received or when an error has been thrown by Netty.
NettyConnection.java
One of the limitations with Netty is the use of the client-server model. This creates a challenge where a P2P model is required. So each NettyConnection will have instances of both server and a client. The client will initiate requests and the server will receive incoming requests. To avoid a N * (N-1) connections, we implement a lookup table that checks to see if a connection is already made to a well known address and reuse the channel if there is a connection established.
Each instance of NettyConnection will have a well known address in the format bind_addr:port. These addresses are the same as those specified in TCPPING. Each message sent by NettyConnection will include the well-known address and will be stored in the receivers and senders look up table. This will create a mapping in the format well-known address -> channel.
Detailed write up on design and implementation can be found in the wiki
See encoding and decoding in the wiki.
The configuration for the Netty pipeline can be seen in the wiki
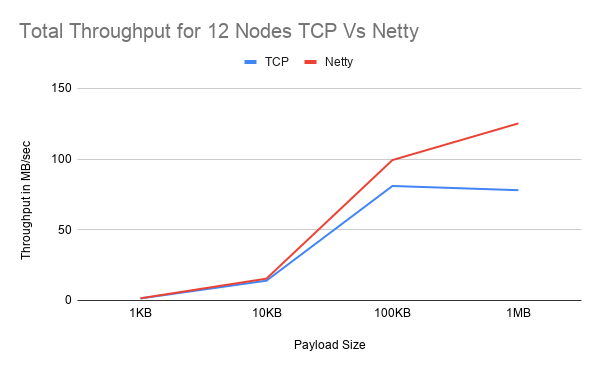
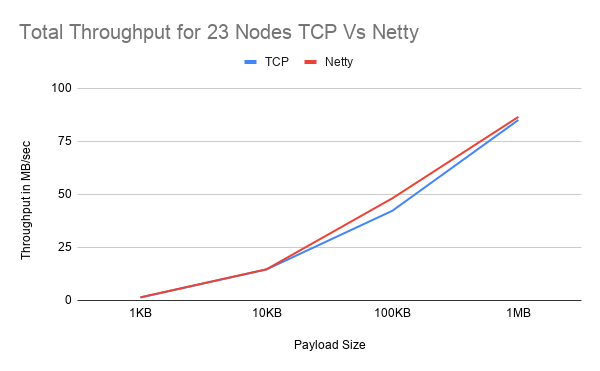
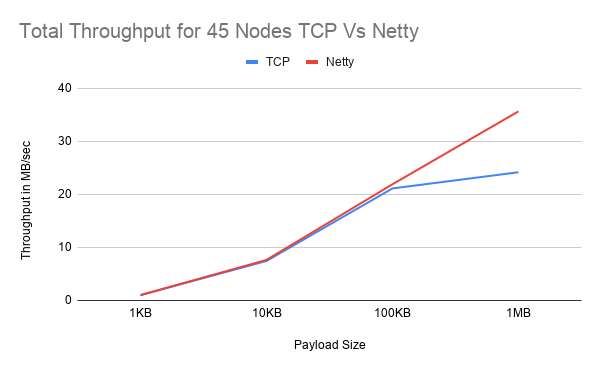
Preliminary Results
Netty seems to increase performance by 14% with a lower thread count and an exponentially increasing payload size but with a higher thread count and increasing cluster size, Netty seems to perform worse. Interestingly in both tests, at 23 nodes, the expected trend does not follow as there is only a small margin of performance increase in the first test and an 11% decrease in performance in the second test. More performnace testsing are on the way.
The following versions were used to measure the throughput of both TCP and Netty.
- VM: Google Cloud N2 machine (General Purpose)
- OS: Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
- Netty Version: 4.1.50.Final
- JGroups Version: 5.0.0.Beta1
- Project build: v0.0.1-perf-test
This test was run with a maximum of 200 and 500 thread per node and repeated 3 times. Unfortunately due to the huge amount of resources required at 45 nodes and 500 threads, the 1MB payload test did not work and so the results are omitted from the graphs and table.
Table of Results
The following tables show the performance difference between TCP and Netty. To calculate the differences the formula shown below was used. The average throughput for each payload and all clusters are shown below.
Difference = ((TCP Throughput - Netty Throughput)/TCP Throughput) * 100
Performance difference for 200 threads
| Payload/Cluster Size | 12 Nodes | 23 Nodes | 45 Nodes | Averages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 KB | 6.80% | 7.04% | 0.99% | 4.95% |
| 10 KB | 10.27% | 0.41% | 2.68% | 4.46% |
| 100 KB | 22.63% | 13.89% | 3.69% | 13.40% |
| 1 MB | 60.56% | 1.70% | 47.44% | 36.57% |
| Averages | 25.06% | 5.76% | 13.70% | 14.84% |
Performance difference for 500 threads
| Payload/Cluster Size | 12 Nodes | 23 Nodes | 45 Nodes | Averages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 KB | 8.70% | -11.02% | -15.49% | -5.94% |
| 10 KB | 9.74% | -11.01% | -11.58% | -4.28% |
| 100 KB | 13.05% | 3.36% | -7.25% | 3.05% |
| 1 MB | 62.77% | 5.42% | - | 34.10% |
| Averages | 23.56% | -3.31% | -11.44% | 6.73% |
The Problem with Low Payloads
It is noteworthy that Netty does not perform well when the payloads are low. The performance is very likely to be low due to the fact that it requires more system calls which is a slow operation. If there are lots of small messages, then there will be lots of system call to flush the message into the network. To solve this problem, we look into the roles Netty's handler and JGroups' bundler play. In this project, some testing has been done to investigate whether Netty’s ability to handle bundling messages is better than JGroups’ ability. To make it explicit, there are four groups. Some results can be found after testing them and comparing the results. The first group is that TCP with JGroups bundler. The second group is TCP without JGroups bundler (It should be configured in the file). The third groups are Netty with JGroups bundler on. The fourth group is Netty without JGroups bundler.
Results of Performances with Low Payloads
| Payload Size | TCP(mb/s) | Netty(mb/s) | Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 B | 0.489 | 0.398 | -18.65% |
| 50 B | 2.412 | 1.964 | -18.57% |
| 100 B | 4.758 | 3.822 | -19.66% |
| 500 B | 20.972 | 17.335 | -17.34% |
| 1 KB | 40.204 | 32.150 | -20.03% |
The results confirm the assumption that TCP outperforms Netty when the payload is small.
Results of Performances with/without Bundlers
The values of differences between with bundlers and without bundlers are actually very subtle. The range of differences is between -1% and 4%. The throughputs of those with JGroups’ bundler and without JGroups bundler are close to each other with every payload. The results indicate that removing the bundler does not actually help with improving Netty’s performance. Therefore, the assumption that Netty’s built-in bundler improves Netty’s performance is wrong. Thus, the useful method to improve Netty's performance with low payloads needs further study.
.png)
.png)
.png)
